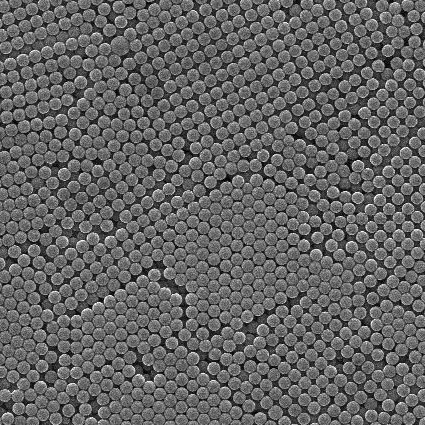
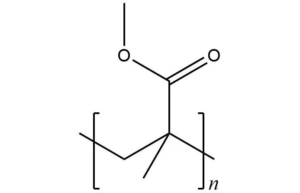
PMMA microspheres, also known as methyl methacrylate microspheres, are white powder particles formed by suspension polymerization of MMA (Methyl Methacrylate) monomers. The structural formula shown in Figure 1 is one of the most important and commonly used materials in acrylic esters, and it is also the most excellent and relatively inexpensive material in the synthesis of transparent materials to date.
It is are widely used in cosmetics, films, coatings, paints, chromatography media, and optical materials due to their specific properties such as large surface area, strong adsorption, high coagulation, and strong surface reactivity. By surface modification, PMMA microspheres with different functional groups can be prepared, including PMMA carboxyl microspheres, PMMA amino microspheres, and PMMA epoxy microspheres. According to application requirements, PMMA microspheres with different degrees of crosslinking can also be prepared.
PMMA microsphere polymer microsphere, as a new research field, began to prepare polystyrene microsphere with uniform particle size and height by Vanderhoff Brand ford of lotion Polymer Research Institute of Lehigh University in 1955, and has made great progress in recent decades. It have unique advantages such as large specific surface area, strong adsorption, high coagulation effect, and the presence of reactive genes on the surface.
They have broad application prospects in many fields such as biomedical materials, chromatographic fillers, and solid-phase organic synthesis. At present, there are many synthesis methods for PMMA microspheres, such as dispersion polymerization, suspension polymerization, lotion polymerization, microemulsion polymerization, atom transfer radical polymerization, soap free lotion polymerization, etc.
The diameter of polymer microspheres prepared by lotion polymerization is from nanometer to submicron. The particle size of microspheres prepared by precipitation polymerization and dispersion polymerization is usually around a few micrometers. The particle size distribution of microspheres prepared by suspension polymerization is generally in the micrometer to millimeter range. The following introduces three synthesis methods.
1.Soap free lotion polymerization
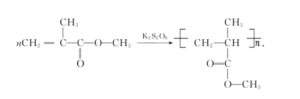
PMMA microspheres were prepared by soap free lotion polymerization with methyl methacrylate as the reactant, potassium persulfate as the initiator, and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate as the surfactant. The reaction formula and mechanism are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
Typically, surfactants are excellent anionic emulsifiers that contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups in their molecules. These amphiphilic structures allow certain insoluble or slightly soluble organic compounds to dissolve in the concentrated hydrophilic groups within the micelles formed by surfactants, significantly increasing the solubility of the substance. It has wide applications in many fields such as washing, medicine and hygiene, petroleum, etc. Li Li et al. explored the influence of surfactants on the preparation of PMMA microspheres by soap free lotion polymerization.
The research results indicate that with the increase of surface active dosage, the particle size of PMMA microspheres gradually decreases and the specific surface area gradually increases. When the concentration of surfactant is 0.025 mol/L, the prepared PMMA microspheres have small particle size, good dispersion effect, and exhibit good thermal stability.
2.Suspension lotion polymerization
Polymethyl methacrylate microspheres are usually prepared by suspension polymerization, but improper control of conditions during the synthesis process can easily cause the particles to adhere and even form blocks, making the reaction difficult to proceed; With the continuous deepening of application research, the application requirements for cross-linked monodisperse polymer microspheres are becoming increasingly high, and the process of large particle size monodisperse narrow cross-linked microspheres is also difficult to control.
Teng Lingzhen et al. synthesized the advantages of suspension lotion polymerization and lotion polymerization, and prepared PMMA microspheres with smooth surface and good size uniformity by comparing different emulsifiers, initiators, rotation speed and other conditions.
The experimental method involves dissolving the initiator in MMA or water, the inhibitor and emulsifier in water, and PVA to form a 5% solution. The mixture is then purged with nitrogen gas in a four necked bottle for 3 minutes, and the aforementioned materials and seeds are added. The mixture is stirred and heated to 75 ℃ to produce PMMA microspheres.
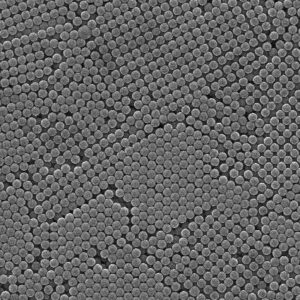
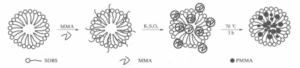
When the water/oil ratio is controlled at 1.4, composite emulsifiers and oil soluble initiators are used, and the rotation speed is controlled at 210-400 r/min, PMMA microspheres with uniform particle size can be obtained under relatively mild conditions, which is the optimal reaction condition. The obtained PMMA microspheres are shown in Figure 4.
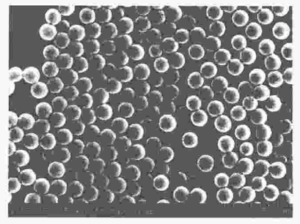
Figure 4 PMMA Electron Microscope Image
3.Dispersed aggregation method
Dispersion polymerization is an effective method for preparing monodisperse microspheres with a particle size of 1-15 μ m, which has wide applications in drug analysis, protein synthesis, flat panel display, and chromatographic analysis.
Dispersion polymerization usually refers to a polymerization method in which monomers are dissolved in a dispersion medium, while the resulting polymer is insoluble in the dispersion medium and stabilized with the help of stereostabilizers (dispersants). It is a special type of precipitation polymerization with controllable particle size. It has the characteristics of good spherical polymer particles, large particle size (compared with lotion polymerization), narrow particle size distribution, low viscosity, etc., and is mainly used for the preparation of functional microspheres.
Jiang Xueliang et al. used methanol/water as the dispersion medium, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as the dispersant, and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator. Under the conditions of no nitrogen protection and no crosslinking agent added, they used a secondary dropwise dispersion polymerization method to easily and quickly prepare micro sized monodisperse narrow distribution non crosslinked PMMA microspheres with a particle size range of 1-4.5 μ m, smooth surface, and good sphericity. The scanning electron microscope image is shown in Figure 5, and the cleaning agent is methanol.
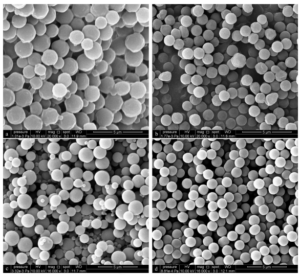
Figure 1 Scanning electron microscopy image of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) microspheres (a) unwashed PMMA microspheres; b, c, d are PMMA microspheres cleaned multiple times)
Examples of PMMA Microspheres Applications
Due to the unique properties of PMMA microspheres, they are widely used in the following fields.
(1) Cosmetics: Improve fluidity; Good tactile sensation and dispersibility; Extinction performance
(2) Paint and ink: scratch resistant agent; Hand feel improvement; Wear resistant agent; Texture agent
(3) Ceramics: pore forming agents
(4) Light diffusion film: light diffusion plate, light diffusion agent
(5) LCD: LCD isolation microspheres
(6) Film: anti adhesive agent; Can be used for PP, PE, PET films
(7) Other: It can also be used as a filler and modifier for plastics, rubber, adhesives, pressure-sensitive paper.