Latex microspheres, also known as polystyrene microspheres, PS microspheres, etc. Polystyrene microspheres are a general term for polymer microspheres formed by self polymerization of styrene or copolymerization of styrene with other monomers with specific functional groups. The surface of polystyrene microspheres has strong hydrophobicity and can undergo physical adsorption with proteins or antibodies. In addition, modifying various functional groups such as carboxyl, amino, epoxy, etc. on the surface of microspheres can enable covalent bonding between microspheres and various biomolecules.
Polystyrene microspheres have broad application prospects in many fields due to the introduction of different functional groups on their surface, which give them advantages such as large surface area, strong adsorption, good mechanical properties, and easy recycling. Among them, polystyrene microspheres (PS) are a common polymer microsphere material, and the preparation and research of polymer microspheres have become a new field of polymer science research. Polystyrene microspheres have the properties of polymer microsphere materials, such as small particle size, large specific surface area, strong adsorption, good dispersibility, and easy modification and modification.
Widely used in fields such as biochemistry, electrochemical detection, catalysts, adsorbents, chromatographic fillers, coatings, etc. There are two main methods for preparing polystyrene microspheres: one is to use high polymers as raw materials and obtain polymer microspheres through certain chemical or physical methods; The second method is to prepare polymer microspheres using monomers as raw materials through various polymerization methods.
Functionalization method of polystyrene microspheres (PS Microspheres):
Due to its low elasticity and lack of polar groups that can adhere to the matrix, polystyrene microspheres are greatly limited in their practical applications. In order to expand their application fields, it is necessary to modify polystyrene microspheres.
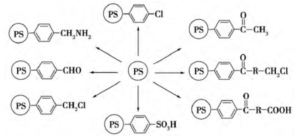
The functionalization methods of polystyrene microspheres mainly involve modification through reactions of benzene rings, olefin double bonds, and specific functional groups.
At present, the functionalization of polymer microspheres can be divided into processing methods and polymerization methods according to different processing methods.
The processing method involves first synthesizing polymer bare spheres, followed by post-processing to obtain functionalized polymer microspheres, including but not limited to swelling, adsorption of functional molecules or particles, to obtain polymer microspheres.
The polymerization method is to initiate the polymerization of monomers and functional monomers while forming surface functionalized polymer microspheres. Its disadvantage is that the high temperature, oxidative initiators, and other reaction conditions during the polymerization process can easily lead to the deactivation of functional molecules.
Functionalized microspheres include common magnetic microspheres, fluorescent labeled microspheres, and surface modified polystyrene microspheres, while surface modified polystyrene microspheres include amino modified, sulfonated modified, and carboxylated modified polystyrene microspheres.
Precautions for using polystyrene microspheres
(PS Microspheres):
Polystyrene microspheres, as a commonly used raw material for biochemical reagents, often generate slag during use. The generation of slag is often caused by improper storage. Even imported microspheres, if not properly maintained, can still have such a situation, which can lead people to mistakenly believe that it is a problem with microsphere preparation.
The appropriate usage method is to wipe the bottle cap and mouth every time it is used, otherwise the residue will easily dry and fall into the bottle to form a precipitate. If not handled, it will block the gun and needle, affect the solid content, and even make it difficult to control the inter batch difference of reagents. The best way is to develop a good habit of wiping off the residue on the bottle cap and mouth after use.
If precipitation is found on the microspheres, the following methods can also be used to solve the problem:
Step 1: Filter cloth filtration – can remove obvious large particles;
Step 2: Low speed centrifugation – remove small particles that are not easily visible to the naked eye;
Step 3: Determine the solid content – first measure the solid content and then adjust it.

.png)