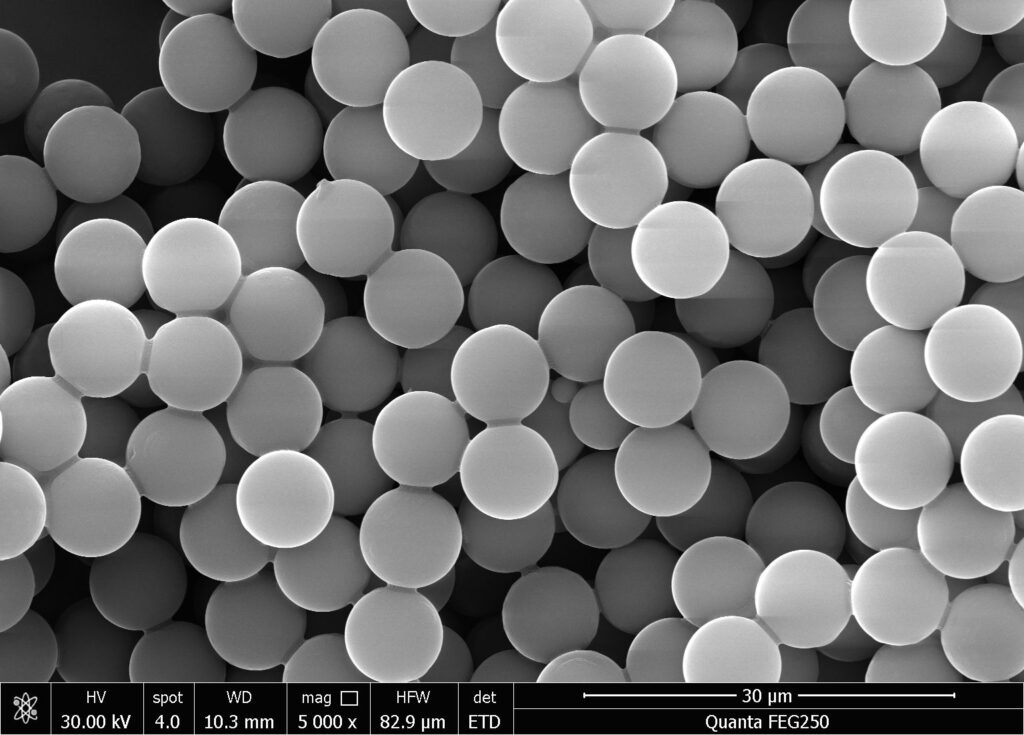
Introduction to Streptavidin Magnetic Beads
Streptavidin magnetic beads (SA beads for short) refer to magnetic microspheres with specific bioactive substances (streptavidin) modified on their surface.Streptavidin magnetic beads are a type of biological nanomagnetic beads with a surface functional group of streptavidin. They can specifically bind to biotin or biotin labeled molecules, thereby separating biotinylated molecules. The strong binding and multi-level amplification effect of biotin avidin with labeling reagents give it the advantages of high specificity and sensitivity, making it widely used in fields such as nucleic acid detection, affinity purification, immunoassay, and cell separation.
Streptomycin is a protein with similar biological characteristics to avidin. Unlike avidin, which is found in egg white, streptavidin originates from the genus Streptomyces and is a protein product secreted by Streptomyces avidin during cultivation. SA can also be produced through genetic engineering. One molecule of streptavidin binds to four molecules of biotin, and the interaction between the two is one of the strongest non covalent binding forces known in nature.
Streptomycin does not contain glycosyl side chains on its surface, and its isoelectric point is closer to neutral, which is conducive to biological reactions. Therefore, its sensitivity and specificity in detection are higher than those of streptavidin, making it more advantageous in applications.
In addition, there is a particularly unique type of neutral affinity magnetic bead, which has a neutral isoelectric point and deglycosylation properties, without RYD recognition sequence. Therefore, its non-specific binding is usually lower than that of avidin and streptavidin, and it maintains the highest specific activity towards biotin binding proteins. Neutral affinity magnetic beads have the lowest non-specific binding and do not reduce biotin affinity.
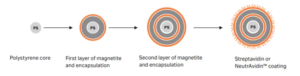
Application of Streptavidin Magnetic Beads
-
Chemiluminescence
streptavidin magnetic beads are very easy to use. After purchase, they are cleaned and diluted to become a component of the luminescent reagent. By mixing with biotinylated antibodies to form a solid-phase capture surface, the target substance in the sample can be captured. The advantages of this system, in addition to the high affinity and amplification effect mentioned earlier, are that biotinylated antibodies are simple and biotin molecules are small, and coupling with antigens/antibodies does not affect protein activity.
There are various commercially available biotinylated reagents available, with the most commonly used being biotinylated molecules containing NHS esters, which rely on the side chains of biotin to form various reactive groups that can react and bind with other molecules (carrying amino, carboxyl, thiol, etc.).
- Targeted capture
Targeted capture sequencing is the process of isolating and enriching target genes from the entire genome, and then using high-throughput sequencing (NGS), which is widely used in health screening, clinical testing, and other applications with high sensitivity. At present, targeted capture sequencing mainly uses liquid-phase capture methods, where biotin carrying probes hybridize with the target region and then bind to streptavidin magnetic beads to achieve capture.
Other fragments are washed off, and then the probes are separated from the target fragments by denaturation. Magnetic separation removes the magnetic beads and empty probes bound to them, completing the capture of the target region. Streptavidin magnetic beads are one of the important raw materials for liquid-phase hybridization capture.
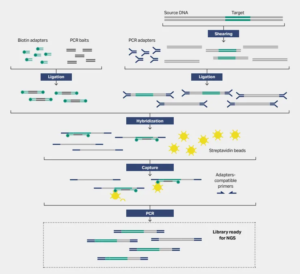
-
Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is a classic method for studying protein interactions based on the specific interaction between antibodies and antigens. Treating a protein as an antigen and using known antibodies against it to precipitate and separate it from a mixed system to achieve preliminary extraction and purification is a method used for separating and detecting specific proteins. In addition to the common Protein A or Protein G magnetic beads, streptavidin magnetic beads are also an option, which only requires biotinylation of antibodies before immunoprecipitation, and then separation and purification using streptavidin magnetic beads.
At the same time, streptavidin magnetic beads are suitable for all types of Pull down reactions, especially for antibodies that cannot bind to Protein A/G, and are therefore widely used in sample preparation and detection development for proteomics applications. In addition, due to the very low non-specific binding of streptavidin magnetic beads, they can also be used in mass spectrometry analysis.
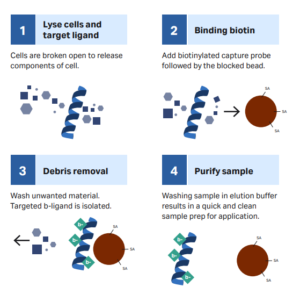
- Cell Separation
A technique that primarily separates a specific subpopulation of cells from a mixed cell sample based on their characteristics. In clinical analysis, whether it is tissue biopsy or blood sampling, cell separation is a critical step because patient derived samples produce complex mixtures composed of a wide range of cell types, matrices, and biological factors. At present, magnetic bead based analyte capture has become a widely used method in cell separation. Through simple magnetic manipulation, it can highly specifically capture target cell populations.
In this process, antibodies are first biotinylated, and magnetic beads bind to biotinylated antibodies through streptavidin, achieving specific binding to the corresponding antigens on the cell surface and indirectly capturing cells by magnetic beads, thus achieving separation. The ideal magnetic beads should not only facilitate cell separation, but also be compatible with a wide range of downstream applications and analyses.
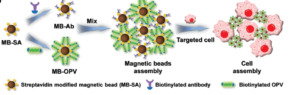
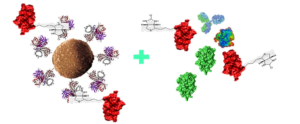
The binding mode of streptavidin magnetic beads to targets:
According to the different target molecules captured and downstream applications, direct or indirect methods can be chosen to capture target molecules. The direct method is to first bind the biotinylated ligand to streptavidin magnetic beads, then incubate with the sample, and finally capture the target through magnetic separation.
It is usually suitable for rapid detection of targets. The indirect method involves the biotinylated ligand first binding to the target molecule in the sample to form a complex, which is then co incubated with streptavidin magnetic beads. After magnetic separation, the target molecule is captured. The indirect method is suitable for experiments with low target concentration, weak specific affinity, or slow binding kinetics, such as NGS targeted capture sequencing applications.
SHBC can provide uniformly sized and superpara magnetic streptavidin magnetic beads. The abundant streptavidin on the surface can efficiently bind to biotinylated molecules, including DNA, RNA, PCR products, antibodies, peptides, and other proteins. Under the action of an external magnetic field, streptavidin magnetic beads are adsorbed, thereby separating from non target molecules in the sample and achieving the capture of target molecules. At present, streptavidin magnetic beads are mainly used in research applications such as nucleic acid capture, protein separation, cell sorting, immunoassay, and targeted sequencing.