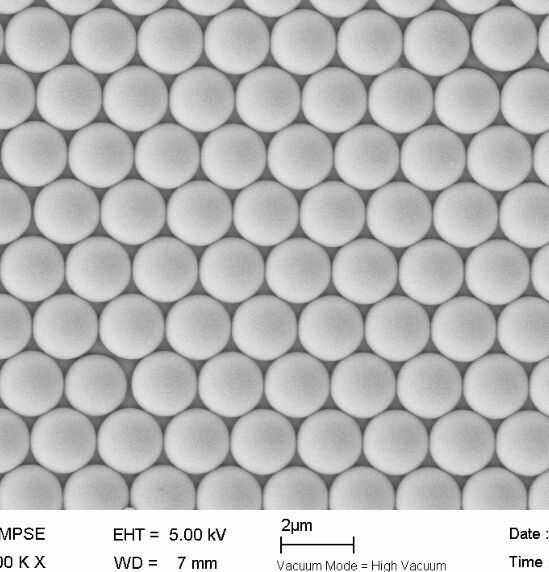
Introduction to Chemiluminescent Magnetic Beads
Chemiluminescent magnetic beads are a type of sandwich structure magnetic beads that contain a porous polymer core, which is coated with special polymer materials to obtain specific surface properties. Magnetic materials are filled in the gaps between the two, which can enable the microspheres to achieve greater buoyancy and uniform particle size; At the same time, different coating materials can also be used to obtain various surface groups, reducing the non-specific adsorption of microspheres, providing a good foundation for reducing background signals and improving sensitivity.
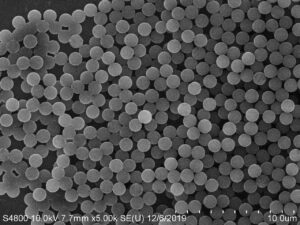
Chemiluminescent magnetic beads have carboxyl, amino, tosyl, and streptavidin (SA) groups based on their surface properties, which can couple with biological molecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and peptides to form stable structures. It can be used in various fields such as magnetic particle chemiluminescence, immunoprecipitation and agglutination, magnetic separation of cells, and nucleic acid specific capture.